Business Responsibility Report
Download the printable version of this section
The Directors present the Business Responsibility Report of the Company for the financial year that ended on 31st March, 2015, pursuant to Clause 55 of the Listing Agreement with Stock Exchanges. The Company also publishes annually, a comprehensive Sustainability Report, based on the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) guidelines.
The details on the aspects discussed in this Report are available in the Company's Sustainability Report. The Company's Board approved Sustainability Policies, ITC Code of Conduct and the Sustainability Report are available on the Company's website - www.itcportal.com.
General Information
| 1. | Corporate Identity Number (CIN) of the Company: | L16005WB1910PLC001985 |
| 2. | Name of the Company: | ITC Limited |
| 3. | Address of the Registered Office: | Virginia House, 37 J L Nehru Road, Kolkata 700 071 |
| 4. | Website: | www.itcportal.com |
| 5. | E-mail id: | |
| 6. | Financial Year reported: | 2014-15 |
| 7. | Key products / services: | |
| Businesses | Products / Services | |
| FMCG | Branded Packaged Foods Businesses (Bakery and Confectionery Foods; Snack Foods; Staples, Spices and Ready to Eat Foods, etc.); Apparel; Education and Stationery Products; Personal Care Products; Safety Matches and Agarbattis; Cigarettes, Cigars, etc. | |
| Hotels | Hoteliering. | |
| Paperboards, Paper & Packaging | Paperboards, Paper including Specialty Paper& Packaging including Flexibles. | |
| Agri Business | Agri-commodities such as soya, spices, coffee and leaf tobacco. | |
| 8. | Locations where business activities are undertaken by the Company: | The Company's businesses and operations are spread across the country. Details of plant locations, hotels owned / operated by the Company, are provided in the section, 'Shareholder Information', in the Report and Accounts. |
| 9. | Markets served by the Company: | ITC's products and services have a national presence and several products are exported. |
| 10. | Subsidiary companies and their BR Initiatives: | The Company has 27 subsidiaries, including 10 subsidiaries outside India. The subsidiary companies define their own initiatives based on their specific context and have access to information and expertise residing with the parent company. |
Financial Details
| 1. | Paid up Capital (As on 31.03.2015): | Rs. 801.55 crores |
| 2. | Total Turnover: | Rs. 49964.82 crores |
| 3. | Total profit after taxes: | Rs. 9607.73 crores |
| 4. | Total Spending on Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR): | Rs. 214.06 crores |
| List of activities in which expenditure in Point 4 above has been incurred: | ||
| Areas listed under Schedule - VII to the Companies Act, 2013 | ITC's interventions (including through Trusts established by the Company) | |
| (i) | Eradicating hunger, poverty and malnutrition, promoting health care including preventive health care and sanitation including contribution to the Swachh Bharat Kosh setup by the Central Government for the promotion of sanitation and making available safe drinking water. | Health & sanitation, drinking water, contribution to Swachh Bharat Kosh |
| (ii) | Promoting education, including special education and employment enhancing vocation skills specially among children, women, elderly, and the differently abled and livelihood enhancement projects. | Education, vocational training, livestock development and livelihoods generation |
| (iii) | Promoting gender equality, empowering women, setting up homes and hostels for women and orphans; setting up old age homes, day care centres and such other facilities for senior citizens and measures for reducing inequalities faced by socially and economically backward groups. | Women empowerment |
| (iv) | Ensuring environmental sustainability, ecological balance, protection of flora and fauna, animal welfare, agroforestry, conservation of natural resources and maintaining quality of soil, air and water including contribution to the Clean Ganga Fund setup by the Central Government for rejuvenation of river Ganga. | Environmental sustainability, soil & moisture conservation and wasteland development |
| (v) | Protection of national heritage, art and culture, including restoration of buildings and sites of historical importance and works of art, setting up public libraries, promotion and development of traditional arts and handicrafts. | Protection of national heritage, art and culture |
| (vi) | Training to promote rural sports, nationally recognised sports, paralympic sports and Olympic sports. | Sports |
| (vii) | Contribution to the Prime Minister's National Relief Fund or any other fund set up by the Central Government for socio-economic development and relief and welfare of the schedule castes, the scheduled tribes, other backward classes, minorities and women. | Contribution to the Prime Minister's National Relief Fund |
| (viii) | Rural Development projects. | Agri development |
Commitment to Sustainable and Inclusive Growth
ITC's sustainability initiatives are inspired by the opportunity to serve larger national priorities through a Triple Bottom Line contribution to the economy. It is the Company's deep conviction that businesses possess the transformative capacity to create far larger societal value by leveraging their entrepreneurial vitality, creativity and innovative capacity. This Vision is manifest in the unique models fashioned by the Company to enable the creation of large scale sustainable livelihoods and the augmentation of natural resources. This Triple Bottom Line commitment of the Company to simultaneously build economic, social and environmental capital has spurred innovation to orchestrate a symphony of efforts that address some of the most challenging societal issues including widespread poverty and environmental degradation. These concerted efforts of the Company over several years have led to the creation of sustainable livelihoods for around 6 million people, many of whom represent the most disadvantaged in society.
While the Company's pioneering work in empowering rural India is a global exemplar, it has also spearheaded several initiatives to achieve new benchmarks in environmental excellence. Recognising that climate change is a threat that particularly makes rural communities extremely vulnerable, the Company has adopted a low carbon growth strategy. This encompasses large scale afforestation, increasing use of renewable energy and a continuous quest to maximise natural resource efficiencies across all its operations. ITC is the only company of comparable dimensions in the world to be carbon positive for 10 years, water positive for 13 years and solid waste recycling positive for 8 years. Its environmental stewardship is also reflected in its luxury hotels being Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED®) Platinum Certified and the increasing share of renewable energy usage in the Company's total energy consumption, which presently stands at 43.1%.
Business Responsibility Policies and Guidelines
Reporting on Sustainability Initiatives
Sustainability Policies and ITC Code of Conduct aligned with Business Responsibility Principles
| ITC Code of Conduct | Freedom of Association |
| Life-cycle Sustainability | Diversity and Equal Opportunity |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Prohibition of Child Labour and Prevention of Forced Labour at the Workplace |
| Responsible Advocacy | Human Rights consideration of Stakeholders beyond the Workplace |
| Product Responsibility | Environment, Health & Safety |
| Responsible Sourcing | Corporate Social Responsibility |
Business Responsibility Report Index on Social, Environmental & Economic Issues
| Sl. No. | BRR Principle | Section in BR Report | Page | Details in ITC Sustainability Report |
| 1 | Businesses should conduct and govern themselves with Ethics, Transparency and Accountability | Corporate Governance for Ethics, Transparency and Accountability | V | √ |
| 2 | Businesses should provide goods and services that are safe and contribute to sustainability throughout their life-cycle | Sustainability of Products & Services across Life-cycle | VI | √ |
| 3 | Businesses should promote the well-being of all employees | Employee Well-being | VIII | √ |
| 4 | Businesses should respect the interests of, and be responsive towards all stakeholders, especially those who are disadvantaged, vulnerable and marginalised | Stakeholder Engagement | X | √ |
| 5 | Businesses should respect and promote human rights | Human Rights | X | √ |
| 6 | Businesses should respect, protect, and make efforts to restore the environment | Protection and Restoration of the Environment | XI | √ |
| 7 | Businesses, when engaged in influencing public and regulatory policy, should do so in a responsible manner | Responsible Advocacy | XIII | √ |
| 8 | Businesses should support inclusive growth and equitable development | Supporting Inclusive Growth and Equitable Development | XIII | √ |
| 9 | Businesses should engage with and provide value to their customers and consumers in a responsible manner | Providing Value to Customers and Consumers | XVI | √ |
Principle 1: Corporate Governance for Ethics, Transparency and Accountability
A Board approved policy provides the framework for ITC's corporate governance philosophy, which is anchored on the values of trusteeship, transparency, ethical corporate citizenship, empowerment, control and accountability. ITC believes that since large corporations utilise societal and environmental resources, governance processes must ensure that they are utilised in a manner that meets the aspirations of stakeholders. ITC embeds sustainability principles in its business strategies, and coupled with corporate governance processes, seeks to ensure superior Triple Bottom Line performance.
The practice of Corporate Governance in ITC takes place at three interlinked levels:| Strategic supervision | by the Board of Directors |
| Strategic management | by the Corporate Management Committee |
| Executive management | by the Divisional / Strategic Business Unit (SBU) Chief Executive assisted by the respective Divisional / SBU Management Committee |
The three-tier governance structure ensures that:
(a) Strategic supervision (on behalf of the shareholders), being free from involvement in the task of strategic management of the Company, can be conducted by the Board of Directors with objectivity, thereby sharpening accountability of management;
(b) Strategic management of the Company, uncluttered by the day-to-day tasks of executive management, remains focused and energised; and
(c) Executive management of a Division or Business focuses on enhancing the quality, efficiency and effectiveness of the business.
ITC's governance framework enjoins the highest standards of ethical and responsible conduct of business to create value for stakeholders.
For more details on ITC's governance structure, please refer to the section, 'Report on Corporate Governance', in the Report and Accounts.
Strategic Supervision of Business Responsibility Practices
The role of the CSR and Sustainability Committee is, inter alia, to review, monitor and provide strategic direction to the Company's CSR and sustainability practices towards fulfilling its Triple Bottom Line objectives. The Committee seeks to guide the Company in pursuing its social and environmental objectives along with crafting unique models to support creation of sustainable livelihoods and environmental regeneration. The Committee formulates, reviews and monitors the CSR Policy and recommends to the Board the annual CSR Plan of the Company in terms of the Companies Act, 2013. The Committee also reviews the Business Responsibility Report of the Company.
The CSR and Sustainability Committee presently comprises the Chairman of the Company and four Non-Executive Directors, one of whom is an Independent Director. The Chairman of the Company is the Chairman of the Committee. The names of the members of this Committee and the number of meetings held during the year are provided under the section, 'Report on Corporate Governance' in the Report and Accounts. The Corporate Management Committee has constituted a Sustainability Compliance Review Committee (SCRC), which presently comprises an Executive Director, two members of the Corporate Management Committee and five senior members of management. The role of the Committee, inter alia, includes monitoring and evaluating compliance with the Sustainability Policies of the Company and placing a quarterly report thereon for review by the Corporate Management Committee.
During the year, four meetings were held to review the implementation of sustainability policies and the progress towards sustainability targets.
Principle 2: Sustainability of Products and Services across Life-cycle
The Company's strategic intent to create enduring value by investing in new engines of growth is powered by its strong and competitive capabilities in R&D, innovation & technology and an array of institutional strengths including deep consumer insights, brand building capability, trade marketing and distribution infrastructure, focus on quality and world-class manufacturing practices, strong rural linkages and outstanding human resources.
The Company endeavours to embed the principles of sustainability, as far as practicable, into the various stages of product or service life-cycle, including procurement of raw material/service, manufacturing of product or delivery of service, transportation of raw materials and finished goods, and disposal by consumers. Policies on 'Life-cycle Sustainability' and 'Responsible Sourcing' detail the Company's approach in this respect.

Some of these elements are discussed briefly below:
Maximising Resource Efficiency
The Company has a long tradition of optimising resource use efficiencies, especially that of common resources such as water and energy. Life-cycle Assessment studies have been carried out for some of the Company's products for identifying additional opportunities to continuously reduce environmental impacts across the value chain. Resource efficiency is integrated into product and process design and is a critical component in the creation of physical infrastructure, operations, logistics and waste management.
The Company's concerted efforts in optimising resource use and efficiency, for instance, are evident across businesses including the Company's most resource-intensive business, the Paperboards and Specialty Papers Division, where continuous improvements in energy and water usage, have made it amongst the most efficient within the sector.
Similarly, the Company's Hotels Division has also demonstrated high levels of resource efficiency by achieving the LEED® (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification at the highest Platinum level for its luxury properties (certification in progress for ITC Grand Bharat which was opened recently). Several of the Company's factories and office complexes have also received the LEED® certification and Bureau of Energy Efficiency's (BEE) star ratings. In order to continually reduce the Company's environmental footprint, green features are integrated in all new constructions and are also being incorporated into existing hotels, manufacturing units, warehouses and office complexes during retrofits.
Sustainable Consumption
The Company has crafted extensive strategies to ensure sustainable consumption of energy, water and other resources in its businesses. Even though the Company's Paperboards and Specialty Papers Division accounts for nearly 90% of the Company's total energy consumption and water intake, it is an acknowledged leader in low-carbon operations as well as in water usage efficiency. This has been achieved by reducing specific energy consumption, increasing share of renewable energy sources, afforestation, recycling and reusing internal and post-consumer waste. The Centre for Science and Environment, New Delhi, rated this business as the 'most energy efficient' in the Indian Paper and Paperboard sector (Challenge of the New Balance, CSE, 2010). In 2014-15, the freshwater intake at the Bhadrachalam unit was 32% below the standard proposed by the National Productivity Council for large-scale integrated pulp and paper mills.
The Hotels Division pioneered the concept of 'Responsible Luxury' and created design interventions, which have enabled optimisation in the usage of energy and water. The LEED® Platinum certification for the luxury hotels of the Company makes 'ITC Hotels' the greenest luxury hotel chain in the world.
For the past 8 years, the Company has been recycling over 98% of the solid waste generated by its units. The Company has laid down comprehensive guidelines on waste management for all its units, which cover hazardous waste as well as e-waste.
Beyond Boundaries

Vendors/service providers and large outsourced manufacturing facilities are encouraged to adopt management practices detailed under the international standards such as ISO 9001, ISO 14001, OHSAS 18001 and ITC's Corporate Environment, Health and Safety (EHS) Guidelines. Contract manufacturing agreements provide for compliance with accepted standards on issues related to EHS, human rights and labour practices. Most of the outsourced manufacturing units of the Foods Business are already HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point) certified and are working towards improvement in energy efficiency. These interventions are some of the examples of the Company's sustainability practices being extended to its supply chain network partners.
In order to strengthen sustainable procurement processes, policies on 'Responsible Sourcing' and 'Human Rights Consideration of Stakeholders beyond the Workplace' have been adopted to address issues of labour practices, human rights, bribery, corruption, occupational health, safety and environment.
The Company works in close partnership with cottage and small-scale units in businesses such as Safety Matches, Agarbattis and Education and Stationery Products. These partnerships have significantly enhanced the competitiveness of a number of units in these sectors. The Safety Matches and Agarbatti Business support the creation of over 18,000 sustainable livelihoods, mainly amongst poor rural women. Similarly, the collaborative supply chain established by the Company's Education and Stationery Products Business provides indirect employment opportunities to over 5,000 people.
Responsible Sourcing
The Company endeavours to integrate sustainability in the procurement process for its products and services across its diversified business portfolio. The policy on 'Responsible Sourcing' encourages resource efficiency in the supply chain which together with the 'Code of Conduct for Vendors and Service Providers' provide guidance to supply chain members and partners to adopt sustainable practices.

Recognising that poverty in rural India also gets accentuated by inadequate access to knowledge, information, price discovery, quality agricultural inputs and markets, the Company has devised unique models for farmer empowerment. These interventions not only support sustainable agriculture and enhance productivity, but also contribute to substantial livelihood creation.
The Company's globally acknowledged ITC e-Choupal initiative has transformed rural communities into vibrant economic organisations by leveraging information technology to provide real-time information on weather, market prices, agricultural best practices etc. It also provides customised extension services and training through 'Choupal Pradarshan Khets' (demonstration farms). Farmers have been empowered through the establishment of integrated rural services hubs called 'Choupal Saagars'. The e-Choupal system has enabled efficient sourcing and raised rural incomes. The Company promotes environmentally sustainable farm practices such as zero tilling, micro-irrigation and watershed development. In addition, the Company promotes large-scale afforestation through its Social Forestry programmes. Customised extension services, knowledge of silvicultural practices, and bio-diversity enhancement enrich the farmers' capacity whilst augmenting natural capital. The farmers are free to transact at will and sell to whoever they choose, though the Company stands as a willing buyer.
Principle 3: Employee Well-being
The Company aims to foster a climate of creativity and innovation to enable its employees enhance value creation for all its stakeholders and to address the challenges of tomorrow with conviction and confidence. The superior capability of the Company's talent pool is premised on a work culture that nurtures quality talent and promotes a conducive work environment that combines the need to focus on performance and results with a caring and compassionate work ethos. Policies on 'Diversity and Equal Opportunity', 'Freedom of Association' and 'Environment, Health and Safety', among others, guide the management approach on specific elements of the Company's work practices.
Equal Opportunity
The Company's policy on 'Diversity and Equal Opportunity' is anchored on its fundamental belief that employees with diverse cultural backgrounds bring unique experiences, perceptions, knowledge and skills of culturally distinct individuals, which when harnessed, strengthens the organisation's productivity and proactively responds to changing conditions. Equally, exposure to new ideas, cultures and perspectives enable the personal growth of employees, based on merit and capability. The policy also ensures a work environment that is free from any form of discrimination amongst its employees in compensation, training and employee benefits based on caste, religion, disability, gender, sexual orientation, race, colour, ancestry, marital status or affiliation with a political, religious or union organisation or majority/minority group.
The Company has put in place suitable processes and mechanisms to ensure that grievances are effectively addressed. The Grievance Redressal Procedure and the Internal Complaints Committee are intended to facilitate open and structured discussions on work related grievances of employees and sexual harassment complaints respectively, to ensure that these are dealt with in a fair and just manner. During the year, 2 complaints of sexual harassment were received, which have since been resolved.
Affirmative Action
The Company is a signatory to the 'CII Code of Conduct for Affirmative Action' which also guides its approach in building human capital on a sustainable basis, through:
- Direct and indirect employment;
- Education, training and skill development to enhance employability; and
- Creation of livelihood opportunities through innovative development models.
Although ITC is committed to employing youth from disadvantaged communities, it is the Company's belief that this can be meaningfully achieved by enlarging the talent pool of youth from these communities by equipping them with the necessary skills and qualifications to enhance their employability in the formal sectors of the economy. The Company lays equal emphasis on strengthening the economic portfolio of poor households belonging to marginalised groups through initiatives aimed at natural resource management and creation of off-farm opportunities to create sustainable livelihoods.
These affirmative action initiatives of the Company have had a direct and tangible impact on 55,061 people belonging to Scheduled Caste/Scheduled Tribes spread over 14 states of the country.
Supporting People with Disabilities
The Hotels Division of the Company has been proactively creating awareness on the opportunities for employing people with disabilities amongst potential employers. In this connection, two handbooks, namely, 'A Guide to Universal Design in Built Environments: A Guide for Creating Accessible Building Infrastructure for Persons with Disability' and 'ITC Hotels Disability Handbook for Industry', have been prepared to guide industry action in this endeavour. Further, the Hotels Business has also employed people with disabilities in various roles.
Learning and Development

For the Company, learning and development is a business critical priority for enhancing capability, strengthening the leadership pipeline and fostering employee engagement. These initiatives enable the Company to achieve sustainable growth. The focus is on achieving continuous performance improvement in functions and businesses and energising the organisation to manage change. Five capability platforms have been identified - Strategic, Value Chain, Leadership, Innovation and Human Resources Development - that are relevant to make businesses future ready. In addition, these platforms are designed to strengthen organisational systems to facilitate speedy and competitively superior responses to market opportunities.
In 2014-15, the Company provided 1,05,277 person days of formal training to employees at various levels. In addition, 29,438 person days of training were dedicated specifically to environment, health and safety issues.
Principle 4: Stakeholder Engagement
The Policy on Stakeholder Engagement provides the approach for identifying and engaging with stakeholders that include shareholders, customers, employees, farmers, suppliers, communities, civil society, media and the government.
The Company believes that an effective stakeholder engagement process is necessary for achieving its sustainability goal of inclusive growth. Accordingly, it anchors its stakeholder engagement on the following principles:
a) Materiality - Prioritised consideration of the economic, environmental and social impacts identified to be important to the organisation as well as its stakeholders.
b) Completeness - Understanding key concerns of stakeholders and their expectations.
c) Responsiveness - Responding coherently and transparently to such issues and concerns.
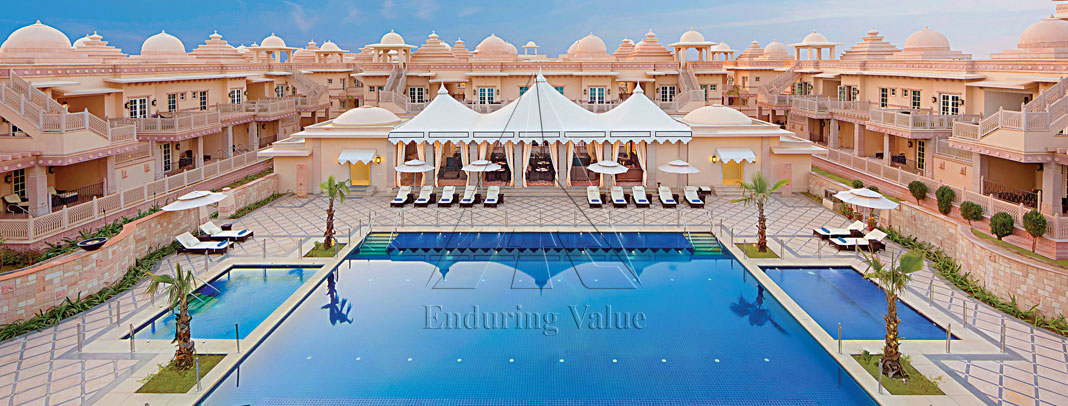
The Company has put in place systems and procedures to identify, prioritise and address the needs and concerns of its stakeholders across businesses and units in a continuous, consistent and systematic manner. It has implemented mechanisms to facilitate effective dialogues with all stakeholders across businesses, identify material concerns and their resolution in an equitable and transparent manner. These measures have helped the Company develop strong relationships, which have withstood the test of time.
The Company's collaborative partnerships with communities are manifest in its programmes such as watershed development, social forestry, animal husbandry services and women empowerment. These initiatives augment the natural resource base of the nation and create sustainable rural livelihoods.

Principle 5: Human Rights
The Company has policies on Human Rights applicable to its employees and its value chains. The policies and their implementation are directed towards adherence to applicable laws and to uphold the spirit of human rights, as enshrined in existing international standards such as the Universal Declaration and the Fundamental Human Rights Conventions of the International Labour Organisation (ILO).
A Grievance Redressal Procedure to address concerns, pertaining to human rights and decent labour practices has been put in place. Awareness inputs were provided to 728 employees on Human Rights Policies and Prevention of Sexual Harassment at Workplace. In addition, 38 Internal Complaints Committee members across businesses were provided skill training on handling cases of sexual harassment at workplace. Employees across the Company are being sensitised to adopt the human rights policies and the ITC Code of Conduct.
The Company has also introduced a Code of Conduct on this aspect for vendors and service providers which has been accepted by such identified parties.
Principle 6: Protection and Restoration of the Environment
The Company is a global exemplar in environmental sustainability and takes pride in being carbon positive, water positive and solid waste recycling positive for many years. The Company has contributed to building environmental security by not only ensuring efficient use of resources but also by augmenting precious natural resources.
The policies on 'Life-cycle Sustainability', 'Environment, Health and Safety' and 'Responsible Sourcing' provide the necessary direction towards climate change mitigation and adaptation efforts as well as natural resource replenishment initiatives. Such efforts include implementation of a low carbon growth strategy across its businesses, integrated soil and water conservation programmes and the creation of large-scale sustainable livelihoods amongst the marginalised sections of society.
The Company has sought to align with the NAPCC (National Action Plan on Climate Change) of the Government of India to respond to the challenges emerging from the threat of climate change. Some of the measures implemented include continual improvement in specific energy consumption (energy consumed per unit of product or service), enhanced use of renewable energy and expansion of forestry projects to improve the Company's positive carbon footprint. The Company has also computed its Greenhouse Gas inventory in line with the ISO 14064 standard, which has been assured at the highest 'Reasonable Level' as per the ISAE 3410 standard, by a third-party assurance provider.
Resource Conservation, Waste Segregation and Recycling
The Company has spearheaded measures across business units to ensure waste minimisation, segregation at source and solid waste recycling. During the year, over 99% of the solid waste generated in the Company's units was recycled. The Company has collaborated with local municipal agencies to work on community waste management in several areas through its Well-being Out of Waste (WOW) initiative.
Water Management Stewardship
The Company has undertaken several water conservation and harvesting initiatives to enhance its positive water footprint. These include continual improvement in specific water intake (water withdrawn per unit of product or service), adoption of benchmarked practices to achieve zero effluent discharge in the Company's operating units and the establishment of rainwater harvesting structures both within the Company's premises and in the catchment areas of its operations. These initiatives not only lower fresh water intake but also maximise groundwater recharge, reduce run-off and provide precious water to farmers. Most of the Company's units have achieved reduction in their specific water intake and many units have recycled their treated effluents in-house and achieved a zero effluent discharge status.
Carrying forward the Company's extensive work on integrated watershed management, an assessment has been carried out at one of ITC's manufacturing units to ensure water security for all stakeholders at the local watershed level. This initiative is intended to further reduce direct water consumption within the unit, influence reduced extraction by stakeholders within defined watershed area, augment groundwater recharge, increase surface storage through the rejuvenation and interlinking of existing water bodies and integrated watershed management measures at catchment area of tributaries. The Company will examine the possibility of extending this initiative to other locations as well.

Cleaner Production Methods, Use of Energy Efficient and Environment-friendly Technologies
The Company is a pioneer in the green buildings movement, which commenced with the establishment of the ITC Green Centre at Gurgaon in 2004 - the highest LEED® Platinum certified building in the world. ITC Grand Chola, the 600-key super-premium luxury hotel complex in Chennai, which is the world's largest LEED® Platinum certified green hotel, has also secured a 5 Star GRIHA (Green Rating for Integrated Habitat Assessment) rating, the highest national rating for green buildings in India. Other large infrastructure investments, such as the ITC Green Centre at Manesar (LEED® Platinum certified) and the upcoming ITC Green Centre at Bengaluru (pre-certified for LEED® Platinum) continue to demonstrate your Company's commitment to green buildings.
The Company has also pioneered the manufacture of Elemental Chlorine Free (ECF) pulp & paper/paperboards in India and taken further steps by introducing 'Ozone bleaching' technology, another first in the country. The Company continues to invest in reducing air emission levels through adoption of cleaner technologies/fuels, monitoring of combustion efficiencies and investments in state-of-the-art pollution control equipment, such as plasma filters, electrostatic precipitators etc. Its units monitor significant air emission parameters, such as Particulate Matter (PM), Nitrogen Oxides (NOX) and Sulphur Dioxide (SO2) to ensure compliance with Company standards that are more stringent than regulatory requirements. The Company has made a commitment to reduce dependence on energy from fossil fuels by progressively moving towards meeting 50% of its total energy requirements from renewable sources by 2020. In order to meet this goal, the Company has developed a strategic approach and plans that focus on both energy conservation and renewable energy investments.
Implementation of Environment, Health & Safety Management Systems

In pursuit of its EHS Policy commitments, the Company has established management systems, certified by accredited agencies in line with international standards like ISO 14001 and OHSAS 18001. Within the purview of certified management systems, contingency plans are developed and implemented to prevent, mitigate and control environmental disasters.
An integrated sustainability database management system implemented across the Company ensures monitoring and reviewing of sustainability performance through defined key performance indicators. Standard operating procedures are in place to define, collate and support audits of data for ensuring accuracy and verifiability. Furthermore, the Company has focused on institutionalising safety as a value-led concept by inculcating a sense of ownership at all levels and driving behavioural change towards creation of a safety culture. In line with this, behavioural based safety initiatives and custom-made risk based training programmes have been implemented at several units which has resulted in improved safety performance.
Principle 7: Responsible Advocacy
The Policy on Responsible Advocacy provides the framework for the necessary interface with Government/Regulatory Authorities on matters concerning the various sectors in which the Company operates. The Company works with apex industry institutions that are engaged in policy advocacy, like the Confederation of Indian Industry, Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry, Associated Chambers of Commerce and Industry of India and various other forums including regional Chambers of Commerce. The Company's engagement with the relevant authorities is guided by the values of commitment, integrity, transparency and the need to balance interests of diverse stakeholders.
The Company, for its social development projects, organises meetings with the local administration and state governments to seek their participation and involvement. Their expert advice and counsel are also sought and approvals obtained, where required, for the planned interventions. The Company also engages in public-private-partnerships (PPP) with the state governments for such projects.
Principle 8: Supporting Inclusive Growth and Equitable Development
ITC's Strategic Stakeholders
The main stakeholders for the Company's social investment programme include:
- Rural communities in the Company's agri-business areas who seek viable solutions to some of the major challenges that threaten the sustainability of their production systems.
- The communities residing in close proximity to the Company's production units, situated in urban and semi-rural locations, who require help in the creation of the necessary socio-economic infrastructure for the emergence of a healthy, educated and skilled workforce with the capability to successfully compete for contemporary jobs.
- The central and state governments, which encourage PPPs to demonstrate scalable and replicable models of development.
Given the Company's operational spread, its stakeholder representation cuts across rural and urban milieus. Interventions therefore have been designed to respond to their unique multi-dimensional development challenges in order to empower stakeholder communities and promote sustainable livelihoods.
The Company's stakeholders are faced with multiple issues, at the core of which are the twin challenges of securing sustainable livelihoods for both rural and urban households:
- Horizon 1: Making today's dominant source(s) of livelihoods sustainable; and
- Horizon 2: Creating capabilities for wealth generation and employment for tomorrow
This has necessitated an integrated approach to development comprising several interventions which are summarised below.
Coverage & Spread
The projects promoted under the Company's social investments programme, numbering 132, are spread over 14 states covering 71 districts. The interventions reach out to over 6.70 lakh households in more than 10,600 villages. Of the total projects implemented, 71% are designed for rural stakeholder households, while the balance 29% address stakeholders residing around the Company's factories.
Strengthening Livelihoods

Watershed Development:
The Company's Watershed Development Programme promotes local management of water resources by facilitating community-based participation in planning and executing watershed projects. A total of 51,397 hectares (ha) was brought under soil and moisture conservation and 1,490 water-harvesting structures were constructed during the year.
Bio-diversity Conservation:
Bio-diversity conservation was promoted in 57 plots covering 504 ha with the objective of protecting the native flora and fauna and provide other eco-system services. In 2014-15, the Company's bio-diversity programme covered 3,191 ha. The Company is now collaborating with several expert agencies, including International Union for Conservation of Nature, to establish baselines, undertake impact assessments and prepare management plans.

Social Forestry:
The Social Forestry programme is designed to promote livelihoods through afforestation by providing financial, technical and marketing support to farmers. It is specially targeted at small and marginal landholders from the economically weaker sections of the society. The total area afforested during the year was 20,355 ha of which 9,241 ha were under agro-forestry, which provides food, fodder and fuel-wood security to small and marginal farmers.
Animal Husbandry & Dairy Development:
The Company has set up 256 cattle development centres in 7 states, which have carried out artificial insemination of 2.24 lakh milch animals during the year. The period saw 80,000 live births, taking the cumulative total of hybrid progenies to 4.79 lakhs. The dairy development programme is assisting farmers to sell an average of 32,000 litres per day of milk, in Munger and Saharanpur.

Improved Agricultural Practices:
The core purpose of this programme is to introduce advanced knowledge and technology through different package of practices and increase awareness of farmers on optimum use of natural resources in order to increase farm productivity and minimise cost of cultivation. 521 farmer field schools were functional during the year which played a pivotal role in disseminating advanced agri-practices to over 21,000 farmers through 7,736 demonstration plots covering over 18,000 ha under different crops. In pursuit of the Company's long term sustainable objective of increasing soil organic carbon, 3,668 compost units were constructed during the year.
Non-farm Livelihoods:
- Micro Enterprises: This initiative of the Company is specifically designed for women from economically weaker sections. This programme provides gainful employment opportunities in micro-enterprises such as Agarbatti rolling/ production in 7 states engaging over 4,000 women. The total raw batti production for 2014-15 was 2,457 tonnes. The scenting units in Munger despatched over 750 million sticks of scented battis during the year.
- Self Help Groups (SHG): Focused work has been initiated on this front with the formation of 375 new SHGs and 2,771 women members in the Company's factory catchments and Natural Resource Management areas. A major thrust was given to financial inclusion of women members by opening bank accounts for 1,335 women. Health camps and bank account opening camps were held for women members engaged in Agarbatti enterprises.
Future Readiness

Education:
The Company's school education programme, with focus on quality and retention, provides access to education to children from weaker sections. During the year, the 'Read India Programme' reached out to 36,000 children and an additional 34,000 children through supplementary learning centres. Over 400,000 children have benefited from this programme. Infrastructure support comprising boundary walls, additional classrooms, sanitation units, furniture and electrical fittings were provided to 147 government primary schools (including Anganwadis), taking the total number of government primary schools covered to 1,158.
Vocational Training:
The Company's programme focuses on building and upgrading skills of youth to better compete with the emerging needs of the job market across different sectors. 13,180 youth were enrolled for training under different courses during the year.
Individual Household Toilets (IHHT):
In order to promote a hygienic environment through prevention of open defecation and reduce incidence of water-borne diseases, 3,578 IHHTs were constructed during the year. In addition to construction, the focus has been on household contribution for increased ownership, community mobilisation and awareness campaigns to instill behavioural changes among the users to progressively eliminate open defecation and create a cleaner environment.
Solid Waste Management:
This programme of the Company is aimed at promoting a clean and green environment through source segregation and recycling of dry waste. It also augments earnings of rag-pickers and waste collectors through increased recovery of dry waste by means of source segregation. Currently operational in Saharanpur, Tribeni and Munger, the focus of the programme is on door-to-door collection of household waste, segregation at site in order to re-cycle and compost so as to minimise the load at municipal dump sites. The programme reached out to over 27,000 households and 2,717 MT of waste was handled, of which only 418 MT of waste was left untreated as municipal dump (15%).
- In addition, the Company's 'Well-being Out of Waste' (WOW) programme, which promotes source segregation and collection, has been implemented in Hyderabad, Chennai, Bengaluru, Coimbatore and some towns of Telangana. The WOW programme reaches out to over 3 million citizens, 500,000 school children, 350 corporates, 1,000 commercial establishments and around 200 industrial plants.
Principle 9: Providing Value to Customers and Consumers
As an organisation which upholds and makes significant efforts to ensure good governance, the Company complies with all relevant laws of the land. The Company's uncompromising commitment to providing world-class products and services to customers is supported by its concern for the safety of its customers/consumers. The Company's overall approach on this vital aspect is guided by its policy on 'Product Responsibility'.
Product Responsibility

The Company is committed to providing products and services that offer best-in-class quality and user experience. With a continually growing portfolio of businesses that use agri/farm products, the Company endeavours to use sustainably sourced ingredients. The Company adopts stringent hygiene standards, benchmarked manufacturing practices and robust quality assurance systems for its products and the declared product shelf-life is determined based on independently validated studies.
Marketing Communication

All businesses of the Company comply with all regulations and relevant voluntary codes concerning marketing communications, including advertising, promotion and sponsorship. The Company's communications are aimed at enabling customers to make informed purchase decisions through factual and truthful disclosure of information. The Company also makes efforts to educate customers on responsible usage of its products and services.
In addition, the Company's businesses have a dedicated consumer response cell to respond to customer queries and feedback on products so as to be able to continuously improve upon its products and services.
Responsiveness to customers
A well-established system is in place for dealing with customer feedback. Consumers are provided multiple options to connect with the Company through email, telephone, website, social media, feedback forms, etc.